ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Playlist AP® Computer Science: Classes and Objects 17 videos
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 1.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following should be declared as a static variable?
In this question, which of the choices correctly constructs a Time(int hours, int minutes, int seconds) object?
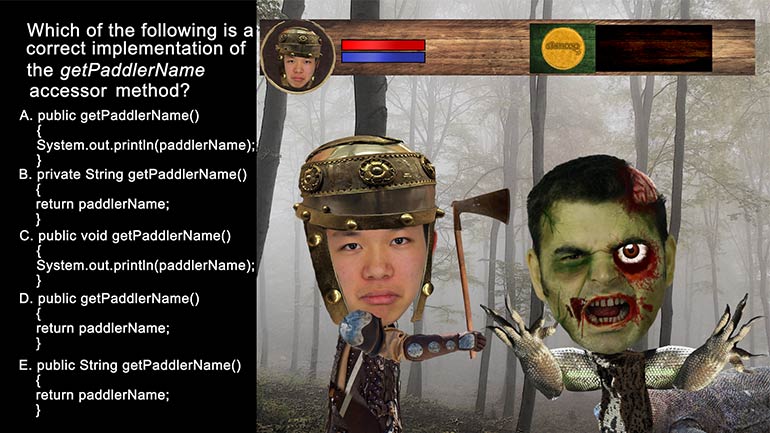
AP Computer Science 3.5 Classes and Objects 187 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 3, Problem 5. Which of the following is not an object?
Transcript
- 00:00
Hurry and here's your shmoop du jour brought to you
- 00:04
by the boy band rivalries of the late nineteen nineties
- 00:07
Not since the civil war has the nation so divided
- 00:10
consider the following declarations album j equals new album no
- 00:15
strings attached and sync two thousand five which of the
Full Transcript
- 00:20
following is not an object In case we get year
- 00:28
ok and hear your potential answers Okay where we where
- 00:32
we live think right again We go back to the
- 00:35
differences between primitive data type can an object classes and
- 00:40
primitive types are not objects And when we talk about
- 00:43
primitive types don't mean grandpa hunt and peck methods in
- 00:46
java There eight primitive data types Remember imagers which store
- 00:50
the whole Numbers in 32 bits of computer memory In
- 00:53
practical terms that means a number of a positive or
- 00:56
negative value of around two point one Four billion with
- 00:59
a b plenty for most uses but its whole numbers
- 01:02
on leah's faras energies are concerned A long is just
- 01:05
like an imager But using sixty four bits of memory
- 01:08
that amount of space could represent a value of over
- 01:11
nine Quintillion again the whole numbers only and if along
- 01:16
Is a longer imager Well you might guess that a
- 01:18
short would be a shorter in inger lever and you'd
- 01:21
be exactly right there you get just sixteen bits to
- 01:24
do your bidding resulting in numbers up to greater than
- 01:26
about thirty two thousand a bite is even shorter than
- 01:30
that eight bits sign that gives you a maximum value
- 01:33
of one hundred twenty seven These smaller data types can
- 01:36
be used to save space in situations where you need
- 01:39
to start a lot of smaller values William data types
- 01:42
are very simple and store only a true or false
- 01:44
value Char stores a single sixteen unicode character or here
- 01:50
meaning practically any alfa numerical punctuation mark symbol or foreign
- 01:54
language character and floats and doubles are floating point values
- 01:59
Floating point values aren't quite exact representations of real numbers
- 02:03
They're more like an approximation but allow you to get
- 02:06
too deep with decimal places good for some things but
- 02:09
when precision is required such as one working with money
- 02:12
use energy instead So far five given declarations which is
- 02:17
not an object alvin j equals new album yet we're
- 02:20
creating a new object of the album class and it's
- 02:22
Called j well this one's an object so it's not
- 02:25
our answer by the way in sync what about backstreet
- 02:29
her and seeing had a couple hits but justin timberlake
- 02:31
was carrying that whole outfit like paul mccartney All right
- 02:36
well string k equals yada yada Well this too is
- 02:39
an object Drinks aren't a primitive data type Their collection
- 02:42
of char data type in array with a few methods
- 02:45
tagging along totally an object during l equals yeah same
- 02:50
thing here drink in equal j get name l that's
- 02:53
an andre too and that leaves into em and as
- 02:57
we know it are not objects their primitive data type
- 03:00
so it leaves us with just option d that's the
- 03:02
answer and a newfound respect for backstreet fact Three back 00:03:07.53 --> [endTime] all right No
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?