ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Science Videos 686 videos
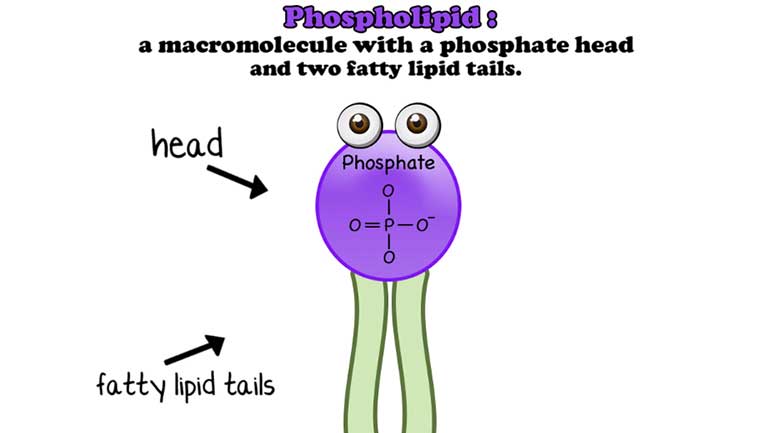
Anything that has a cell (bacteria, listen up!) has phospholipids that keep the cell contained and give it form and shape. Phospholipids protect us...
GMOs. Now that’s a scary word. Or is it? Guess it’s time to ask ourselves: WWMST? ...For those of us who don’t constantly ask ourselves “wh...
AP Biology 3.4 Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 32 Views
Share It!
Description:
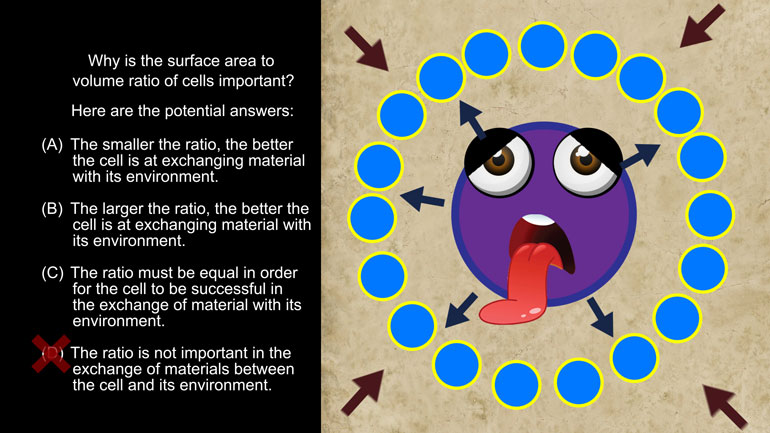
AP Biology 3.4 Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks. Why is the surface area to volume ratio of cells important?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here’s your shmoop du jour, brought to you by nutrients…
- 00:06
…so much healthier for you than oldtrients. [woman eating food and face turns green]
- 00:09
Maybe clean out the fridge once in a while…
- 00:12
Why is the surface area to volume ratio of cells important?
- 00:16
And here are the potential answers: To say that the ratio is NOT important in
Full Transcript
- 00:23
the exchange of materials between the cell and its environment is just oh so wrong.
- 00:27
The ratio between the surface area and volume of cells has a gigantic impact on the behavior,
- 00:31
physiology and other qualities of their environment.
- 00:34
Like when your lungs expand and contract to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. [lungs expanding and contracting]
- 00:38
So, breathe easy, Shmoopers, Answer D is incorrect. [a couple with their arms out wide on a beach]
- 00:42
Answer C is also suspect.
- 00:44
Size and shape affect the ability of diffusion to supply the demands of the cell.
- 00:49
Having an equal surface area-to-volume ratio would inhibit the necessary flow of materials
- 00:53
across plasma membranes.
- 00:55
Cells need breathing room to diffuse more oxygen and take in the nutrients they crave. [a cell struggling to breathe]
- 01:00
Answer C is not the ratio that cells have in mind for a peaceful existence.
- 01:04
So is a smaller surface area to volume ratio better than a large ratio?
- 01:09
Or is it better the other way around?
- 01:11
Remember that surface area is very important to cell function because everything the cell [Inside of a cell with arrow showing nutrients enter here]
- 01:15
could possibly want makes its way through the cell membrane.
- 01:18
As the size of a cell decreases, the ratio of surface area to volume increases. [a green cell decreasing in size]
- 01:23
As a result, small cells are more efficient at diffusion because of their high surface [one green cell multiplies into 5 cells]
- 01:27
area to volume ratio.
- 01:28
A long, thin cell like a nerve cell is a perfect example of efficiency.
- 01:33
On the other side of the coin, when a cell increases in size, the surface area expands [A green cell increasing in size]
- 01:37
at a lower rate than the volume.
- 01:39
Based on that, the correct answer is B, the larger the ratio, the better the cell is at
- 01:44
exchanging material with its environment.
- 01:47
It also explains why protozoa should never be the size of a school bus. [A protozoa bus picking up school girls]
- 01:51
They would starve to death because they would have a hard time getting enough oxygen, water
- 01:56
and nutrients transported across their plasma membranes. [Gigantic cell destroying a city with laser vision]
- 02:01
Besides…like the creators of Godzilla won't need any more inspiration for their horror movies…
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
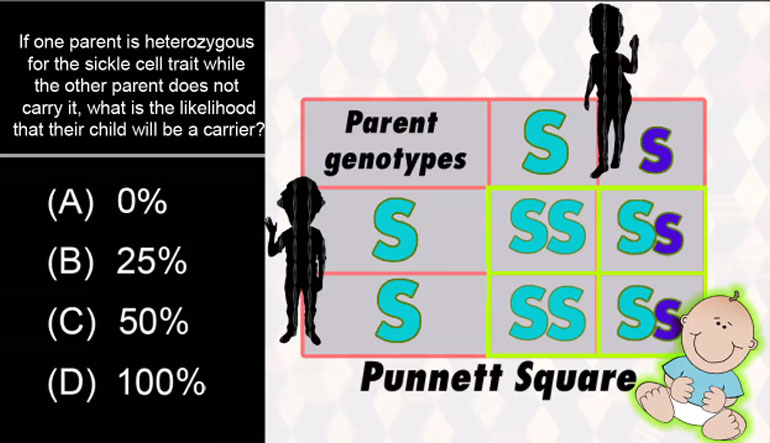
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
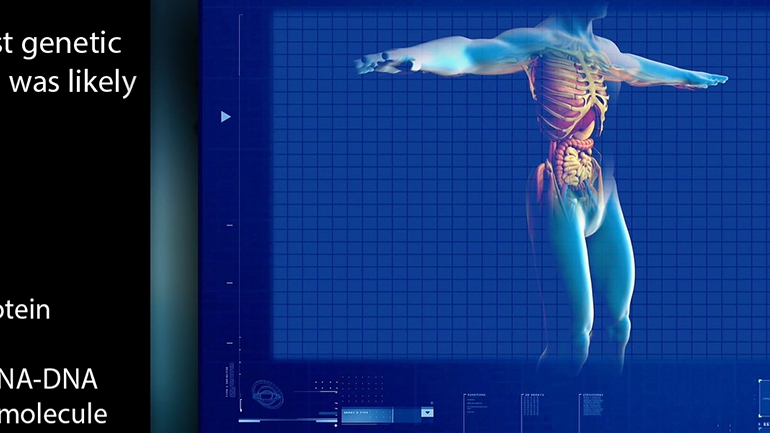
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?