ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Science Videos 686 videos
In this video, we dive beneath the sea to review the kinds of interesting animals that live in the deep blue.
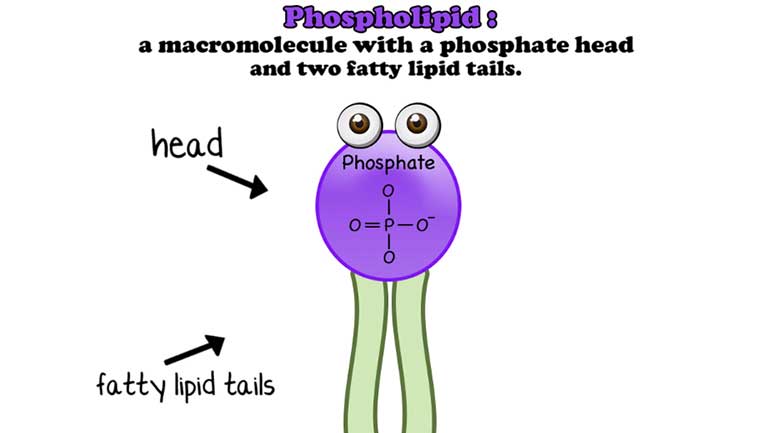
Anything that has a cell (bacteria, listen up!) has phospholipids that keep the cell contained and give it form and shape. Phospholipids protect us...
Molecular Genetics: Mitosis vs. Meiosis 443 Views
Share It!
Description:
In this video from our course on molecular genetics, learn about mitosis, meiosis and the difference between the two.
Transcript
- 00:00
[ whoosh ]
- 00:01
We speak student!
- 00:03
[ whoosh ]
- 00:05
Molecular Genetics
- 00:07
Mitosis versus Meiosis
Full Transcript
- 00:10
A la Shmoop
- 00:12
So we're here talking about DNA replication now
- 00:15
with Dr. Ruth Tennen, who is a guru on the subject.
- 00:17
So, Dr. Ruth, what are the two main types of cells
- 00:21
in the human body?
- 00:22
So there's two types.
- 00:24
One is the somatic cell.
- 00:26
So, those are kind of the regular cells that you think about.
- 00:28
So, your liver cells or your skin cells. Muscle cells.
- 00:32
The other type is germ cells, or sex cells.
- 00:35
And those are the cells that combine to form a new human. [egg and sperm combine to make a new human]
- 00:38
[ crowd oohs ]
- 00:39
Got it. So "somatic" - S-O-M-A-T-I-C.
- 00:43
Where does that -- what's "som"?
- 00:44
- It's not from "South and Market," right? - No.
- 00:46
It was done before that.
- 00:47
What is somatic?
- 00:49
So "soma" means body.
- 00:50
So it's basically body cells.
- 00:51
Got it.
- 00:53
Okay. So how do somatic cells relate with germ cells?
- 00:58
Are they sort of coopetition? Are they frenemies?
- 01:01
Are they just -- do they hate each other?
- 01:03
Do they live separately?
- 01:05
They're pretty happy together. They're in different parts --
- 01:06
So, basically, your whole body is composed of somatic cells
- 01:08
and then just sperm and egg cells.
- 01:09
Those are the only germ cells you have.
- 01:11
And the germ cells are what ultimately combine to form your body.
- 01:15
So they're required to form the somatic cells also.
- 01:17
And how does a germ cell -- cause, you know,
- 01:19
a normal person, you think "germ, ooh, that's bad.
- 01:21
I wanna not have any germs."
- 01:23
But, in fact, that would be bad, right?
- 01:25
Bad to not have germ cells, yeah.
- 01:27
It would be difficult to reproduce if you were a human.
- 01:28
Hmm. So we need the germs to reproduce?
- 01:32
- Right. - That just seems counterintuitive, but take it. There.
- 01:35
Okay, next. Five-dollar word - mitosis.
- 01:39
We touched on this a little bit earlier.
- 01:40
But give us a good definition for mitosis.
- 01:43
So, mitosis is the process of cell division that somatic cells undergo. [cells divide]
- 01:48
They take their duplicated DNA and they divide it into two new daughter cells.
- 01:51
[ ding! ]
- 01:52
Got it. So this is like the pants zipper thing
- 01:54
with the ATCG?
- 01:55
So, it's a little bit after that.
- 01:57
During -- if you think about the cell cycle,
- 01:59
which is basically how a cell goes from one to two cells,
- 02:01
it starts off by replicating its DNA.
- 02:04
And then at another point in the cycle is when the mitosis happens.
- 02:06
And mitosis is just basically the physical separation
- 02:08
of the DNA into two daughter cells.
- 02:11
Got it. Okay.
- 02:12
Then what's "meiosis"? M-E-I-O-S-I-S.
- 02:16
"Me-osis" or "my-osis" is basically the same idea as mitosis,
- 02:19
but it's for the germ cells, or the sex cells. [egg and sperm]
- 02:21
And it's a little bit different because meiosis starts with
- 02:25
- a normal cell that has two copies of every gene. - Mm-hmm.
- 02:28
And then there are two stages of meiosis -
- 02:30
one and two. And, ultimately, at the end, you end up,
- 02:32
rather than having two copies, just having one copy of each gene in the cell.
- 02:35
And that's what the egg and the sperm are.
- 02:36
One copy that can combine to ultimately form a diploid cell.
- 02:40
Got it. Fair enough.
- 02:42
Okay. Wow. DNA replication.
- 02:44
A la Dr. Ruth.
- 02:48
What are the two main types of cells in the human body?
- 02:52
What is mitosis?
- 02:54
What is meiosis?
Related Videos
In this video, we dive beneath the sea to review the kinds of interesting animals that live in the deep blue.
Anything that has a cell (bacteria, listen up!) has phospholipids that keep the cell contained and give it form and shape. Phospholipids protect us...
GMOs. Now that’s a scary word. Or is it? Guess it’s time to ask ourselves: WWMST? ...For those of us who don’t constantly ask ourselves “wh...