ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Computer Science Videos 112 videos
Just as you move your furniture into a new house before spending the night, you’ve got to spend a little time setting up your environment when yo...
Doubles and ints. At first glance, it may look like this video will be about baseball and football statistics. But they're actually computer scienc...
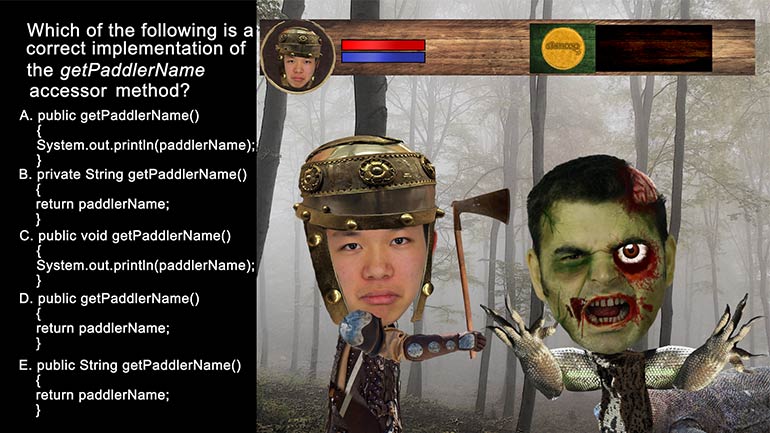
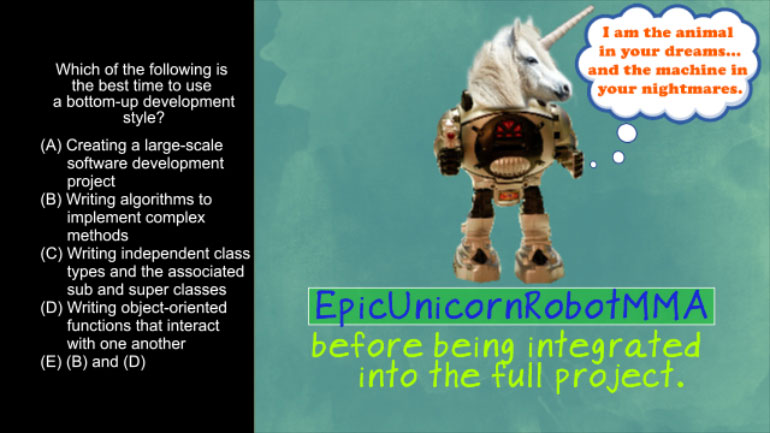
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 3.1 Review of the Basics 168 Views
Share It!
Description:
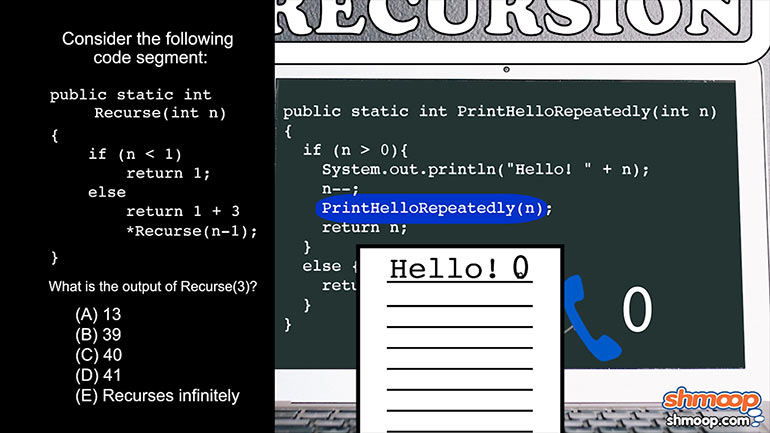
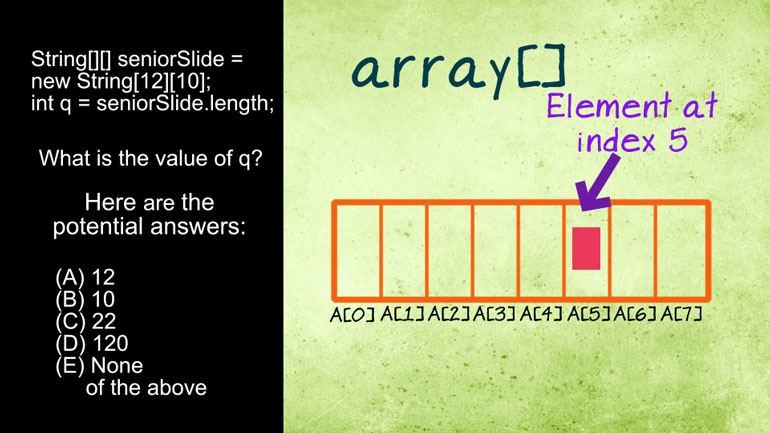
AP Computer Science 3.1 Review of the Basics. What can you expect about the outcome from running this code?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your smoke Use your
- 00:05
brought to you by double variables double the precision Double
- 00:10
the things you have to worry about All right Well
- 00:12
what can you expect about the outcome from running this
- 00:14
code This coat right here and here The pencil answers
Full Transcript
- 00:19
shmoop overflowed running All right so let's go let's Start
- 00:25
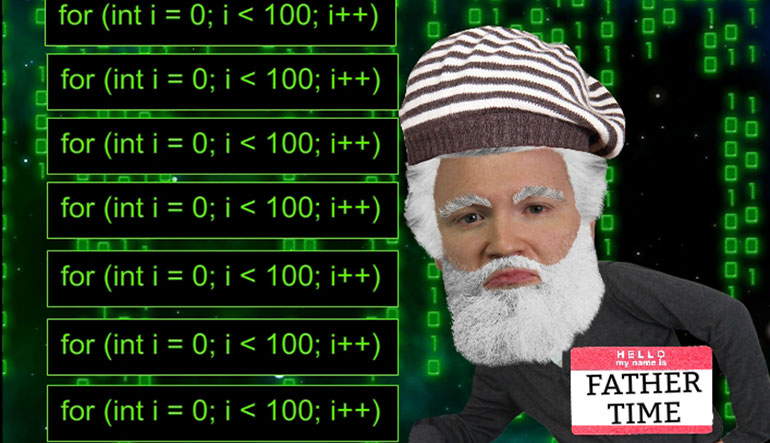
with a look at what This coat actually does Step
- 00:27
by step we'll first we create a double variable called
- 00:30
numb with the value is your appoint one Then we
- 00:33
begin a four loop that starts with an injured eye
- 00:35
at zero stops when eyes no longer less than one
- 00:38
hundred and increment i by one Each time the loop
- 00:41
is run Essentially this loophole run one hundred times each
- 00:44
son loop cycles we make numb equal the value of
- 00:47
one divided by num minus nine point nine Phillips put
- 00:50
real numbers to it This means for the first generation
- 00:53
one divided by num a zero point one would equals
- 00:57
ten Got it one by one then ten minus nine
- 01:01
point nine his point one And we're back where we
- 01:03
started so Luke will run 99 more times and since
- 01:06
none will always equal point one when we cycle the
- 01:09
result will always be point one again In theory we're
- 01:13
dealing with a double variable here double means double precision
- 01:17
floating point variable got it and floating point variables aren't
- 01:22
the rigid representation of riel numbers we might expect In
- 01:26
fact the floating point bearable is more like a very
- 01:28
good guess at a very precise number It's never quite
- 01:32
exact even the very simple point one plus point two
- 01:35
in floating point variables wouldn't give you a point Three
- 01:38
you get something like point three zero zero for or
- 01:44
thereabouts hearts let's try something if you have your compiler
- 01:47
handy add the following lines to this code and run
- 01:51
it and we'll see what happens if you don't have
- 01:53
your compiler handy well and just we'll put system out
- 01:57
front line number right here in the loop That way
- 02:00
it'll print the current value of numb each time the
- 02:03
loop cycles and we'll be able to see how it
- 02:05
changes over time and for those not ableto participate Well
- 02:09
here's a picture of wild turkey these things you're huge
- 02:11
all right and here's what The result looks like weird
- 02:15
Right What happened Well the imperfections in the floating point
- 02:20
operations kept magnifying themselves over and over and over getting
- 02:24
worse and worse and loris with each iteration before finally
- 02:27
settling in at negative ten Those faras our potential answers
- 02:31
go option a Yep they're being overflowed No no overflow
- 02:35
ares occurred Option b there will be under flow so
- 02:39
after running numb will equal zero Also no option c
- 02:43
after running numb will equals your appointment Well sure the
- 02:46
code may look like things will remain in zero point
- 02:48
one on paper but using a floating point variable means
- 02:51
the exact value of zero point one is not gonna
- 02:54
happen Option d after running none will not equal zero
- 02:58
point one Well that's right For a moment it even
- 03:01
seemed like num was equal to just about everything but
- 03:03
zero point one option e both andy well no ass
- 03:07
for overflow and there was no So our answer is
- 03:09
d and we're number one or rather we're number one 00:03:12.768 --> [endTime] point lobo too
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
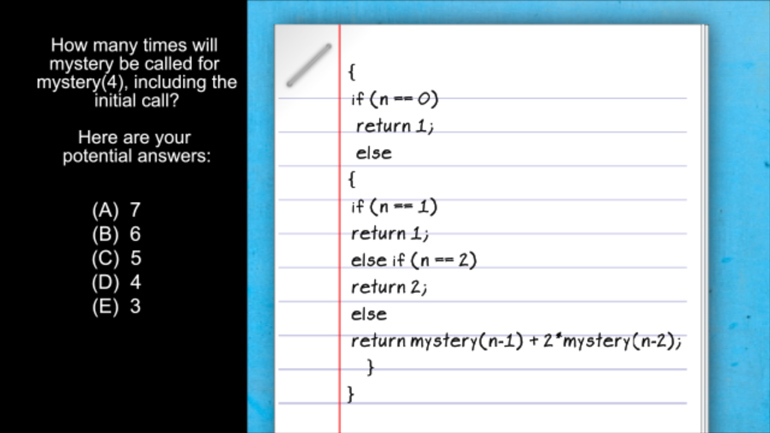
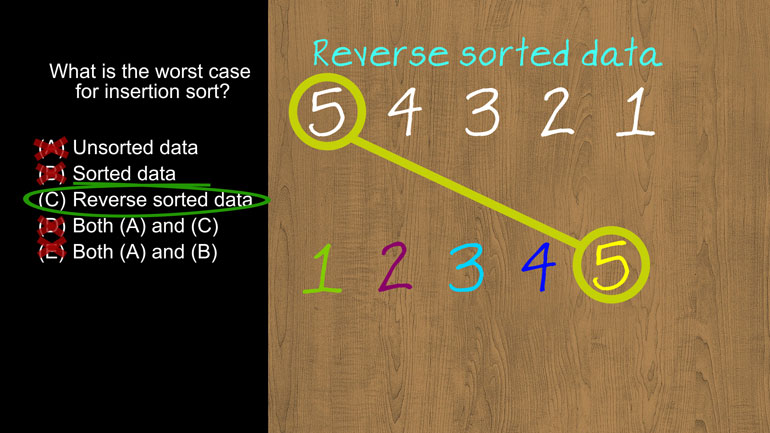
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
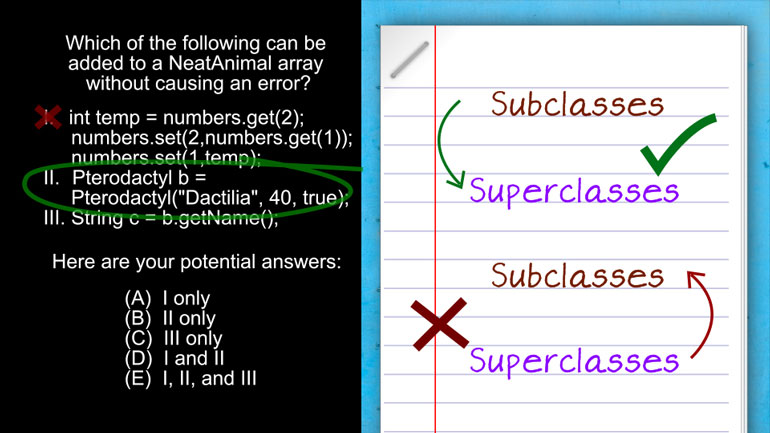
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?