ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Computer Science Videos 112 videos
Just as you move your furniture into a new house before spending the night, you’ve got to spend a little time setting up your environment when yo...
Doubles and ints. At first glance, it may look like this video will be about baseball and football statistics. But they're actually computer scienc...
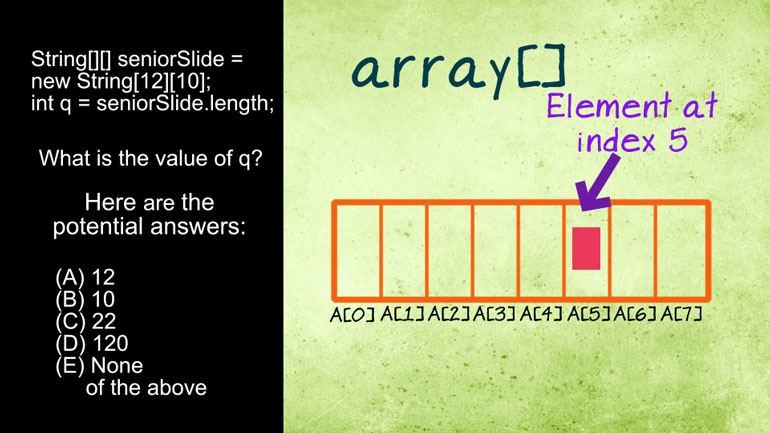
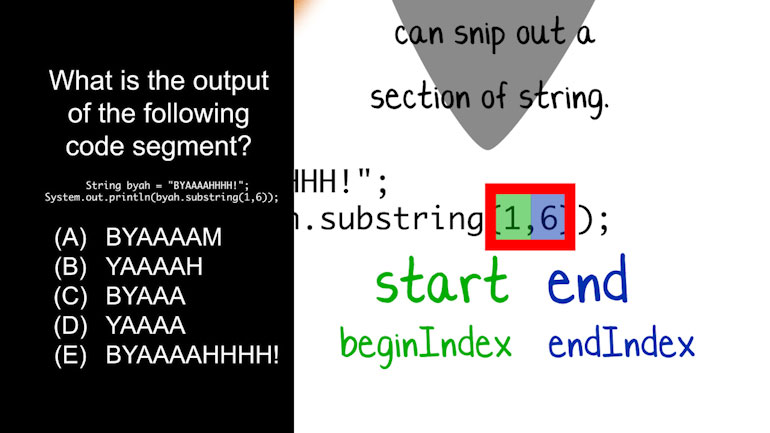
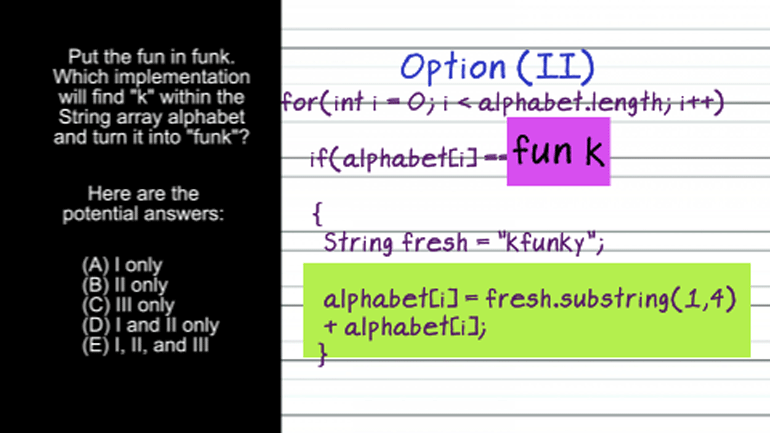
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Review of the Basics 242 Views
Share It!
Description:
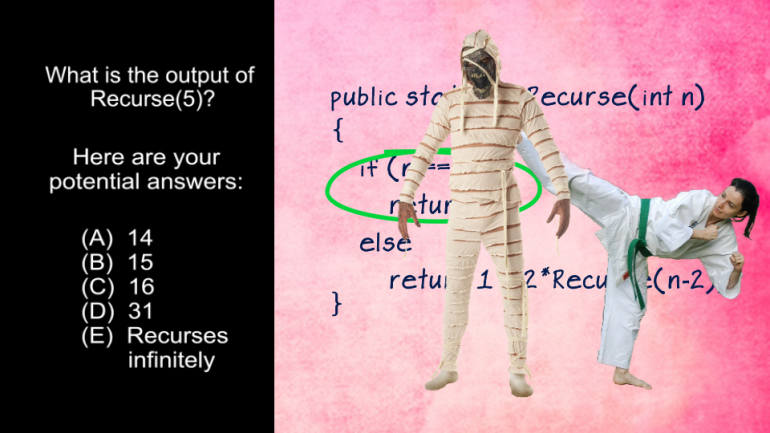
This AP Computer Science drill asks what the value of Num2 is after a specific code is executed.
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by flooring values but not the kind
- 00:08
you find at the used carpet place All right what
- 00:11
is the value of numb to after the following code
- 00:14
is executed All right And here the potential answers Here
Full Transcript
- 00:22
we go It looks like that bit of code converts
- 00:24
to a value from its initial data type of double
- 00:28
two imager than to double again and back to imager
- 00:31
So the key here is in knowing what happens the
- 00:33
values when you convert values between data types but wait
- 00:36
isn't a number just a number Well why is the
- 00:39
imager six eight four four different from the double six
- 00:43
eight for four why're there different data types at all
- 00:48
Well the answer lies in your computer's memory or more
- 00:50
accurately how your computer treats these different types Imagers air
- 00:55
pretty simple data types They use thirty two bits four
- 00:57
bites of memory to store a numeric value ranging from
- 01:01
around two million ish or so to negative two million
- 01:04
ish space is limited however so there's no room in
- 01:08
those thirty two bits to stored decimals it's all whole
- 01:11
numbers A double uses twice the amount of computer memory
- 01:15
Sixty four bits or eight bites Now there's room for
- 01:18
decimals and way way larger values But at what cost
- 01:22
Well because computer memory is not infinite all those bits
- 01:25
at if we're not calculating extremely large numbers or decimal
- 01:28
values in our program were probably wasting our memory by
- 01:31
using doubles Another important thing to know is when you
- 01:34
converted data type with a decimal such as a double
- 01:37
to an imager you not only lose the decimal but
- 01:39
the number is floored rather than rounding to the nearest
- 01:43
number That means even if you're converting a double like
- 01:46
four point nine three into an imager it comes out
- 01:49
to four rather than the five you might have otherwise
- 01:51
expected So think of it like a huge gnarly acts
- 01:55
like sing the numbers decimal point off with no regard
- 01:58
for what's on the right side of it Yeah you
- 02:00
ever been to a circumcision been like that now let's
- 02:04
get to the bottom of our problem starting with the
- 02:06
innermost parenthesis into being negative Three point five gives us
- 02:11
negative three because again we're flooring it and watch your
- 02:15
fingers or other important body parts Then we do negative
- 02:18
three times point five and convert it to a double
- 02:21
so that'll be negative One point five negative one point
- 02:24
five converted to an injurious florid against we get negative
- 02:27
one and our answer is b and hey watch Where 00:02:30.46 --> [endTime] you're swinging that thing pal
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
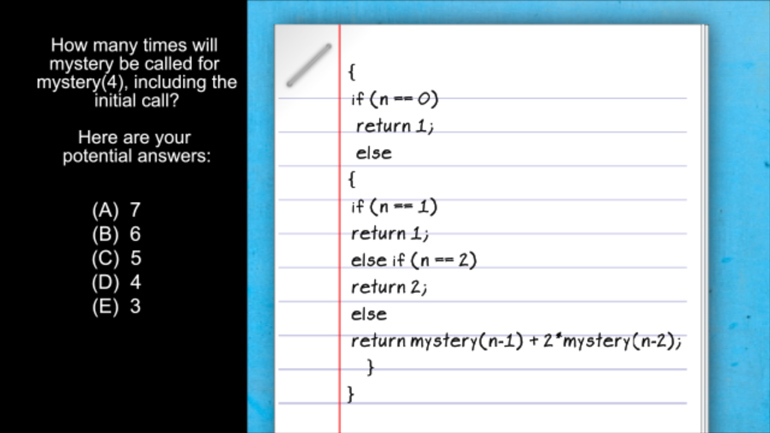
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
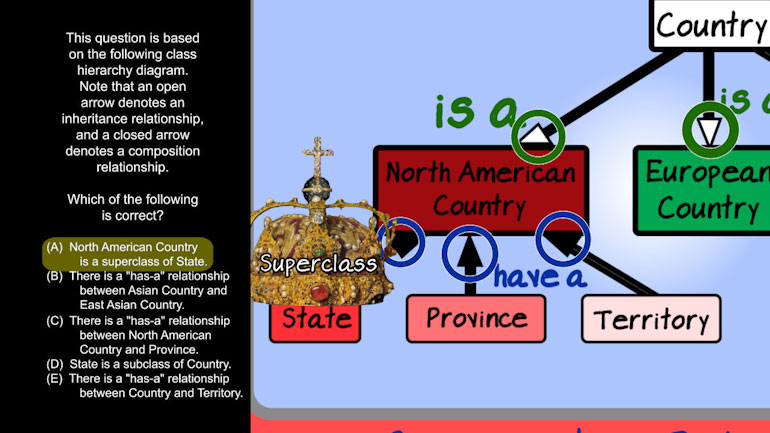
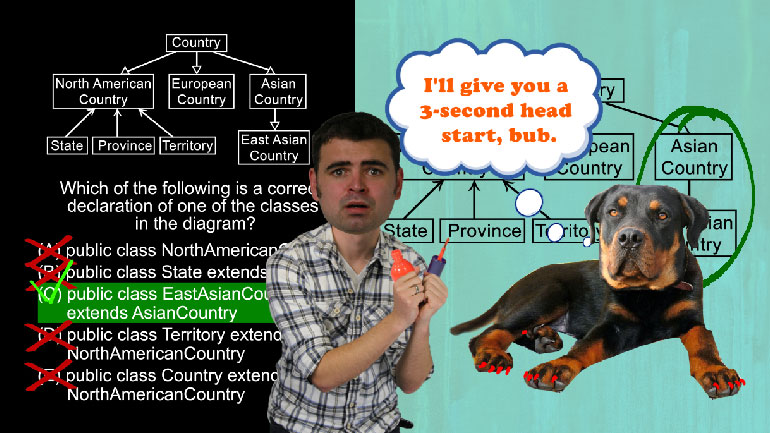
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?