ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Computer Science Videos 112 videos
Just as you move your furniture into a new house before spending the night, you’ve got to spend a little time setting up your environment when yo...
Doubles and ints. At first glance, it may look like this video will be about baseball and football statistics. But they're actually computer scienc...
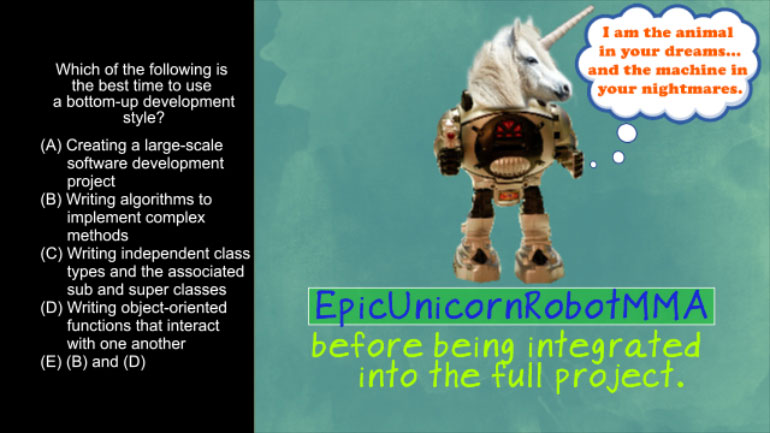
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 4.1 Review of the Basics 175 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Computer Science 4.1 Review of the Basics. Which of the following is an object?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your smoke du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by primitive data types Careful they bite
- 00:09
Consider the following declaration Doubleday is one point six one
- 00:14
eight string act is just moving true art which of
- 00:19
the following is an object and wrong time Your potential
Full Transcript
- 00:23
answers Arthur now just what in the sam hill is
- 00:30
what you might be saying especially if you're an old
- 00:32
timey gold prospector Well java is an object oriented language
- 00:36
Doesn't that mean everything's an object Well not quite There
- 00:40
are objects that contain data but they're also primitive data
- 00:44
types in job there a primitive data types to choose
- 00:47
from so don't worry about memorizing them all But what
- 00:50
sets them apart from objects is that they're composed of
- 00:53
no other data types and can't be broken down any
- 00:56
further their basic unbreakable building blocks like the atoms of
- 01:00
the programming world you know Well pirate in nineteen forty
- 01:03
five Come on Okay so double and julian are primitive
- 01:08
data types And on lee contain data But string is
- 01:12
an object that contains data as well as some other
- 01:14
stuff Ride java string apart and you'd find that it's
- 01:17
actually an array of character primitives wrapped up in a
- 01:21
single object along with some methods for accessing those characters
- 01:25
Yeah charge Ok it's Not quite like comparing apples to
- 01:28
oranges it's More like comparing apples the boxes of apples
- 01:32
and some other stuff Your answer is b two on
- 01:35
lee But why Why even have permanent data types at
- 01:38
all Why didn't jobs creators just make everything an object
- 01:41
and leave it at that well efficiency reasons with an
- 01:44
object you could wind up allocating memory in unpredictable ways
- 01:48
Primitive data types are straight forward Each one has a
- 01:51
specific size that it'll take up in memory no necessary
- 01:55
when you're working with lots and lots of individual values
- 01:58
but use an object with all the methods and baggage 00:02:00.985 --> [endTime] that comes with it And well oh boy who
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
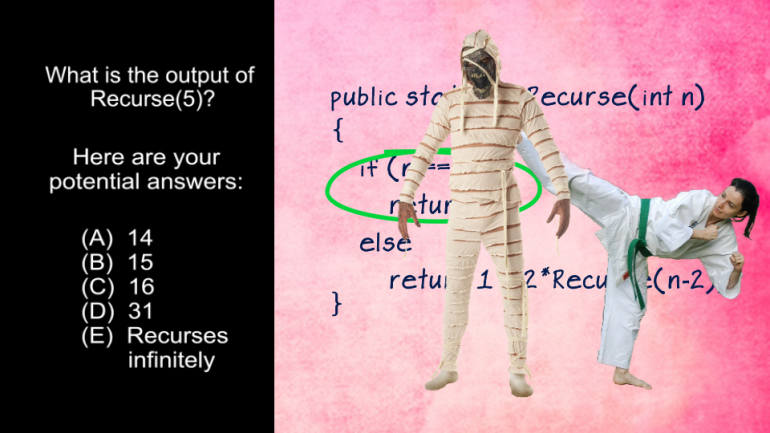
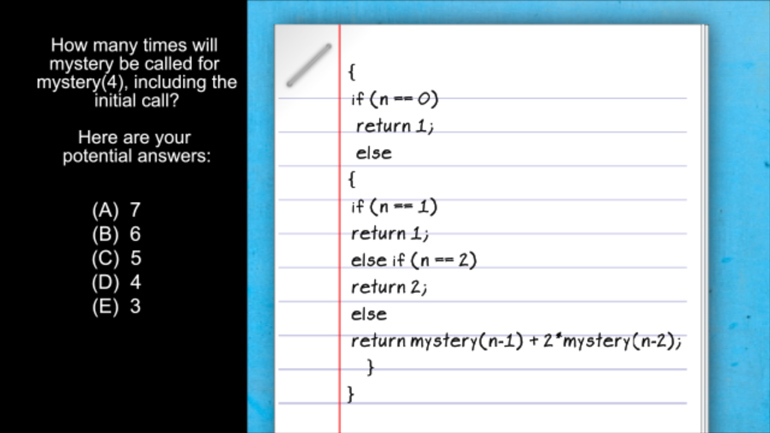
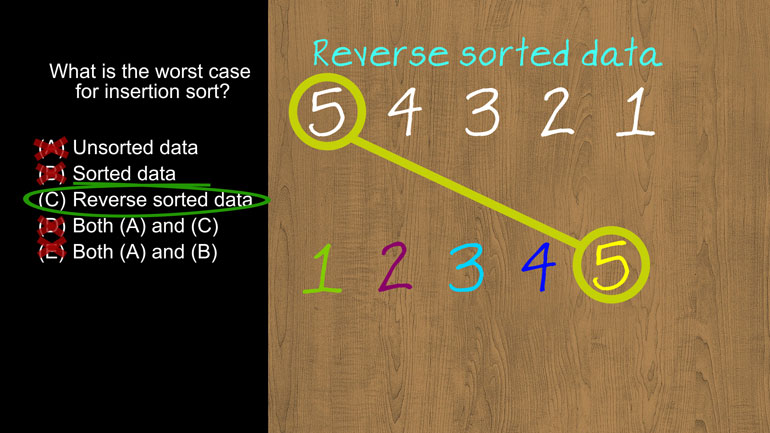
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
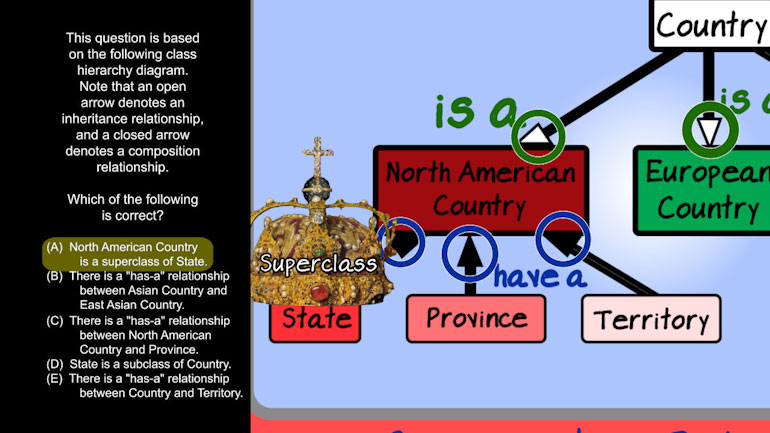
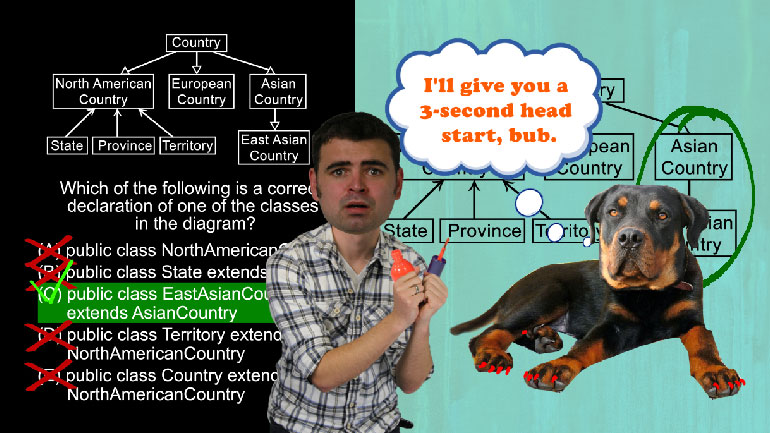
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
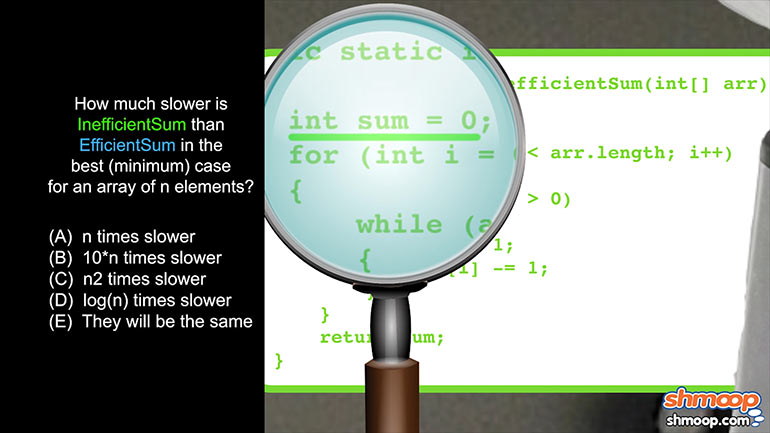
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?