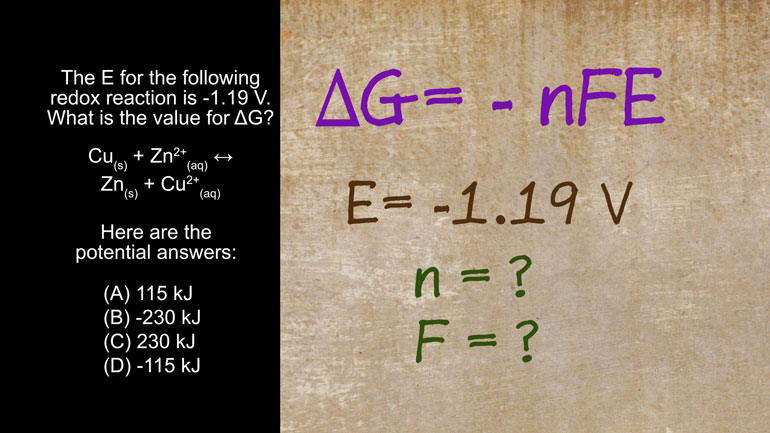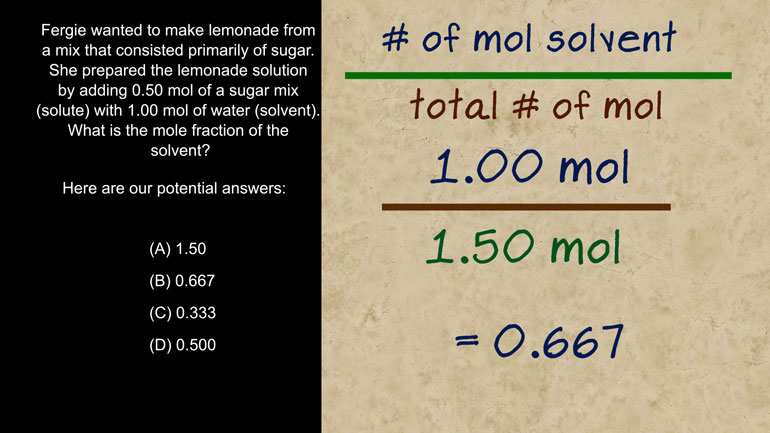ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Test Prep Videos 443 videos
ACT Science: Research Summary Passage Drill 2, Problem 1. Why do you think that the filter paper will not remove the salt from the water?
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
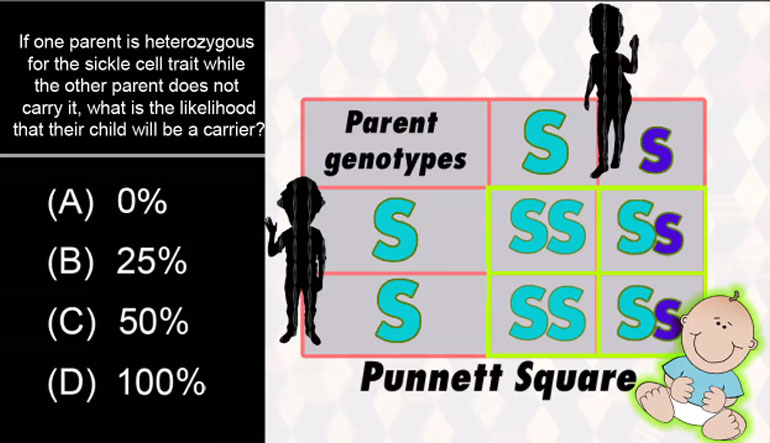
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Chemistry 2.3 Laws of Thermodynamics 6 Views
Share It!
Description:
This is a question about Gibbs free energy. You'd better act fast though. Otherwise, you may have to pay the normal sticker price of $99.99.
Transcript
- 00:03
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by free energy.
- 00:06
It’s like a free lunch, except, you know, it actually exists. [Girl approaches pizza store]
- 00:10
Okay, here's our question.
- 00:12
For ?G to have a negative value 100% of the time, ?H
- 00:18
and ?S should be which of the following, respectively?
Full Transcript
- 00:23
And here are our potential answers.
- 00:25
All right, well, the change in Gibbs free energy, or ?G, tells us whether
- 00:30
or not a chemical reaction is spontaneous. [Scientists working in a lab]
- 00:31
Not in the romantic way.
- 00:34
In the science way.
- 00:35
Though flowers are always a nice gesture…take notes, chemical reactions… [Scientist holding bunch of flowers]
- 00:40
If ?G is negative, the reaction is spontaneous.
- 00:44
If it’s positive, the reaction is not spontaneous and we have to add energy to get the reaction
- 00:49
to proceed. [Man holding glassware of chemical and goes up in flames]
- 00:50
We’re sure there’s a message about optimism in there somewhere.
- 00:54
Anyway, this question is asking us for the signs on ?H and ?S so that ?G is always negative,
- 01:02
and the reaction is always spontaneous.
- 01:05
So, what in the world are ?H and ?S, and what do they have to do with free energy?
- 01:09
No, it’s not hours and seconds, and no, free energy is not a sports drink. [Man holding energy on a track]
- 01:13
?H and ?S are thermodynamic quantities, and for this problem we care about how they relate
- 01:19
to ?G.
- 01:21
What we have to do is recall the Gibbs free energy equation.
- 01:24
We want to know when ?G is negative.
- 01:27
What do we have here?
- 01:28
This looks like a complex inequality. [Complex inequality example]
- 01:30
…No?
- 01:31
Not ringing a bell?
- 01:33
Go read up on complex inequalities. [Man reading a book]
- 01:35
We’ll be sitting here, waiting patiently.
- 01:38
Now let’s think about the necessary signs of ?H and ?S in order for this inequality
- 01:43
to always be true.
- 01:45
Add T?S to both sides to simplify the inequality.
- 01:47
Inequality – easy to simplify in science, not so much in life.
- 01:49
When using the Kelvin temperature scale, we know T is always positive. [temperature thermometer increases]
- 01:53
Multiplying by T won’t change the sign of the right hand side, so we can simply consider
- 01:58
the signs of ?H and ?S.
- 02:01
What signs on these variables make this inequality always true? [Girl standing with mathematical signs]
- 02:05
Let’s look at our options.
- 02:06
Let's check out A, for example.
- 02:07
If ?H and ?S are both positive, is the inequality always true?
- 02:12
If you can think of a scenario to disprove the inequality, then your answer is no.
- 02:17
The only scenario that can’t be disproven is choice (D).
- 02:21
The left hand side of the inequality is always negative, and the right hand side is always
- 02:26
positive, meaning the inequality is always true.
- 02:30
Because, you know, a positive number is always greater than a negative number. [Guys holding positive and negative number signs]
- 02:34
And there’s our message about optimism.
- 02:36
And now you know a little bit more about Gibbs free energy.
- 02:39
And if you happen to come across a free lunch, please… let us know. [People cue outside a store for free lunch]
Related Videos
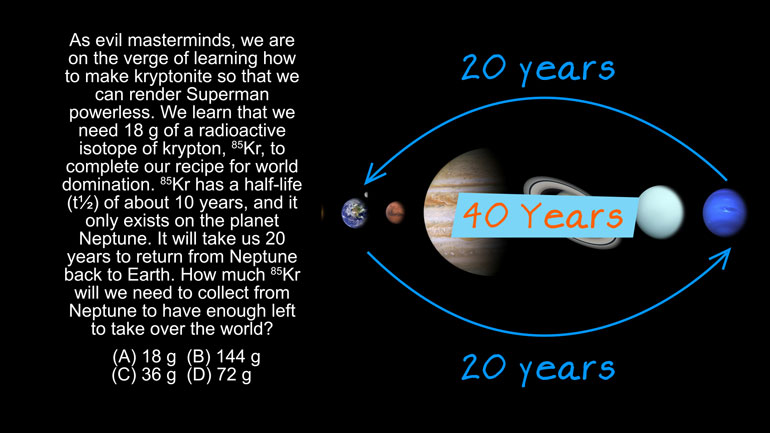
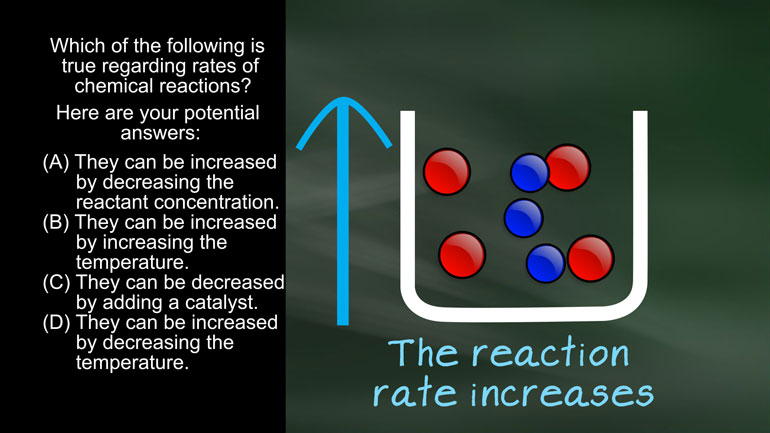
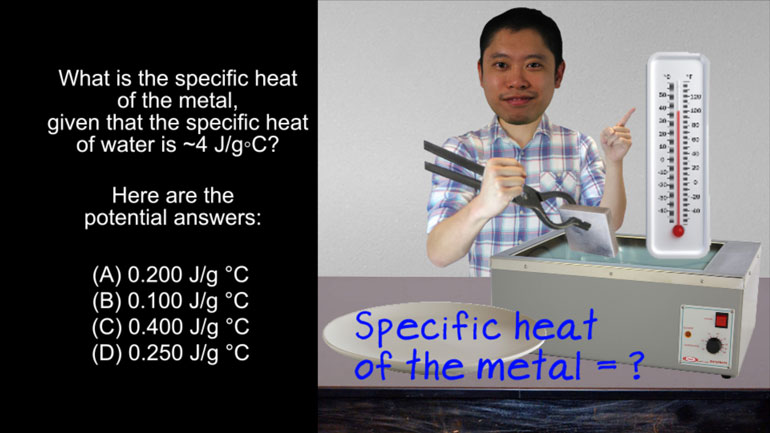
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?